Bridging the Translational Gap: How 3D Engineered Heart Tissues Are De-Risking Cardiac Drug Discovery
By the Curi Bio Team
A 24-well Mantarray plate featuring 3D engineered heart tissues (EHTs) tethered between flexible pillars for functional contractility analysis.
For decades, cardiovascular drug discovery has struggled with a fundamental challenge: the models used to validate targets do not "speak human." While traditional 2D cell cultures have been industry workhorses, they fail to predict clinical outcomes. Approximately one-third of new drug candidates fail in clinical trials due to unexpected cardiotoxicity.
At Curi Bio, we believe reducing this attrition requires a paradigm shift toward New Approach Methodologies (NAMs) that prioritize human biological relevance. We are leading this charge with 3D Engineered Heart Tissues (EHTs).
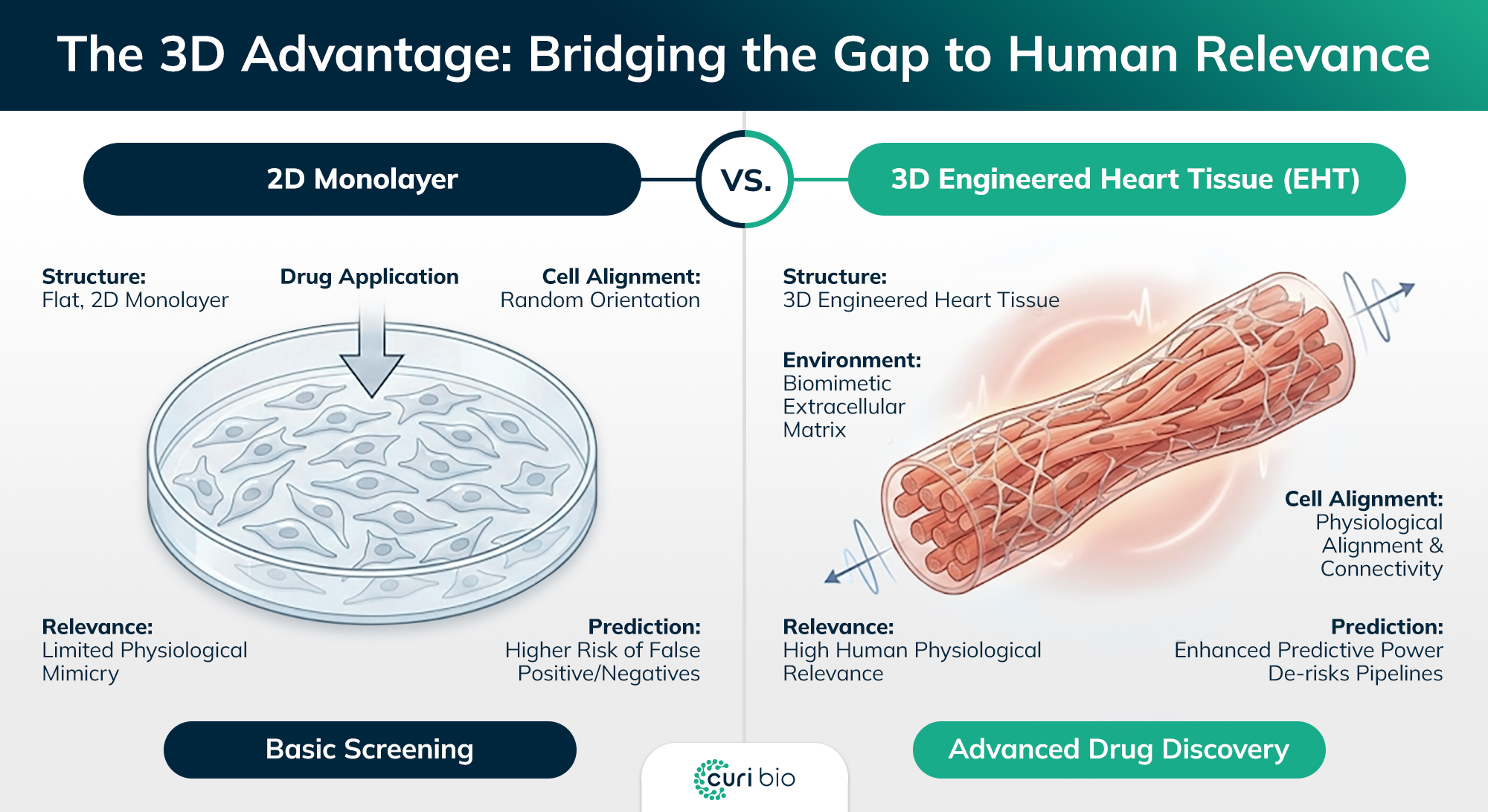
Why 2D Monolayers Fail to Predict Human Physiology
To understand the necessity of 3D EHTs, we must first diagnose the limitations of incumbent 2D technology.
Morphology Mismatch: Native cardiomyocytes are rod-shaped and aligned; 2D cells are random and polygonal, resulting in disorganized sarcomeres.
The Metabolic Gap: Standard 2D hiPSC-CMs typically remain in a fetal-like glycolytic state, making them less sensitive to drugs targeting mitochondrial function.
Twitching vs. Work: 2D models lack the load-bearing capabilities (preload and afterload) required to develop adult-like contractile kinetics.
Comparison of disorganized 2D cardiomyocyte monolayers vs. uniaxially aligned 3D human heart tissues showing physiological maturation.
The 3D Advantage: Replicating the Living Heart In Vitro
The transition to 3D EHTs is a restoration of physiological context. The Curi Engine™ leverages three pillars of bioengineering to close the translational gap.
1. Structural Alignment: Engineering Anisotropy
The Mantarray™ platform utilizes a proprietary casting method that tethers cell-laden hydrogels between flexible pillars. This structural maturity allows for the precise measurement of longitudinal contractile force, enabling the detection of subtle effects that 2D models miss.
2. Biochemical Cues: Promoting Metabolic Maturation
Curi Bio’s Cardiac Muscle Tissue Media (CBCM) replicates the in vivo environment. Data indicates that EHTs cultured in CBCM generate 4-5x stronger contractile forces compared to standard media.
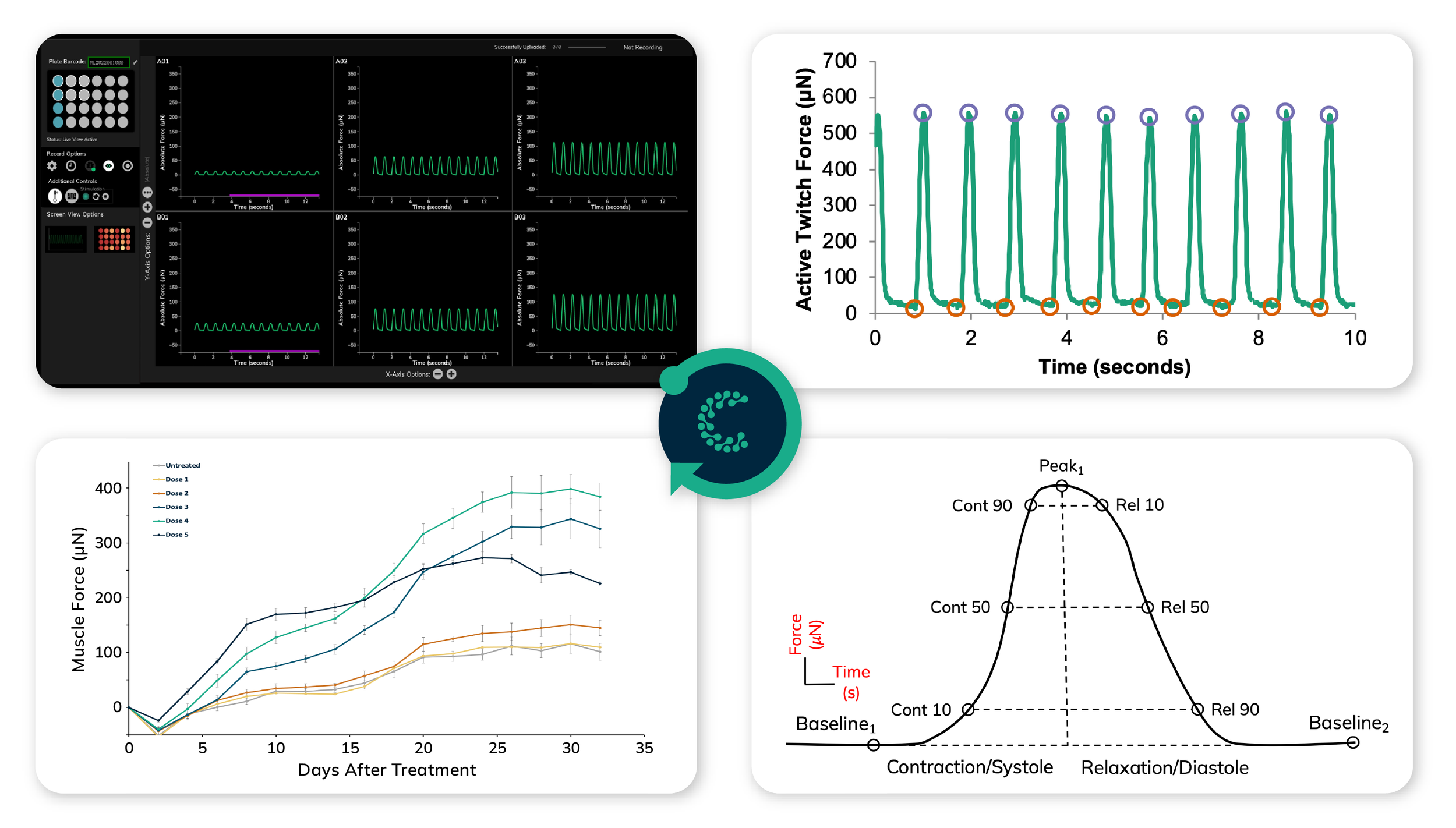
3. Functional Quantification: The Power of Multimodal High-Throughput Screening
The Curi Engine integrates two complementary systems:
Mantarray (Contractility): Measures absolute force, contraction velocity, and relaxation kinetics in parallel across 24 tissues.
Nautilai™ (Electrophysiology): Captures calcium transients and voltage propagation at up to 1500 Hz to detect pro-arrhythmic events.
Standardized data output from Pulse Analysis Software showing contraction and relaxation kinetics for human-relevant cardiac drug screening.
Case Studies: 3D EHTs in Action
Genetic Cardiomyopathy (MYBPC3): 3D EHTs demonstrated that AAV9-mediated gene therapy reversed cardiac hypertrophy and improved systolic function.
Chronic Cardiotoxicity (Doxorubicin): Because Curi Bio’s EHTs remain viable for weeks, they allow for chronic dosing regimens that reveal latent toxicities missed by acute 2D assays.
The Economic and Regulatory Driver
The FDA Modernization Act 2.0 authorizes the use of NAMs, including organ-on-chip models, as alternatives to animal testing. A cost analysis by Moderna (2023) revealed that toxicity studies using human-relevant organ-on-chip models cost approximately $325,000 compared to $5.25 million for studies using non-human primates.
Conclusion: De-Risking the Future
The transition to 3D EHTs is an upgrade in confidence. By embracing structural alignment and metabolic maturity, Curi Bio empowers researchers to make go/no-go decisions based on human-relevant data.
Ready to modernize your discovery pipeline?
Contact our expert team to schedule a consultation.